Integrating Roboflow with Cognex Dataman Cameras
An advantage of BarcodeSink is that it makes it easy to add custom computer vision to a system using Cognex Dataman devices. This tutorial shows you how to send your images to Roboflow. If you've got an old Cognex device laying around or you want to update your computer vision software without changing out your facility's existing hardware, read on.
Setting Up Roboflow
Before we program our Cognex camera to send images to Roboflow, we need to create a workflow.
Once we create a workflow, we'll be prompted to pick a model type. For this tutorial, we'll choose an object detection model.
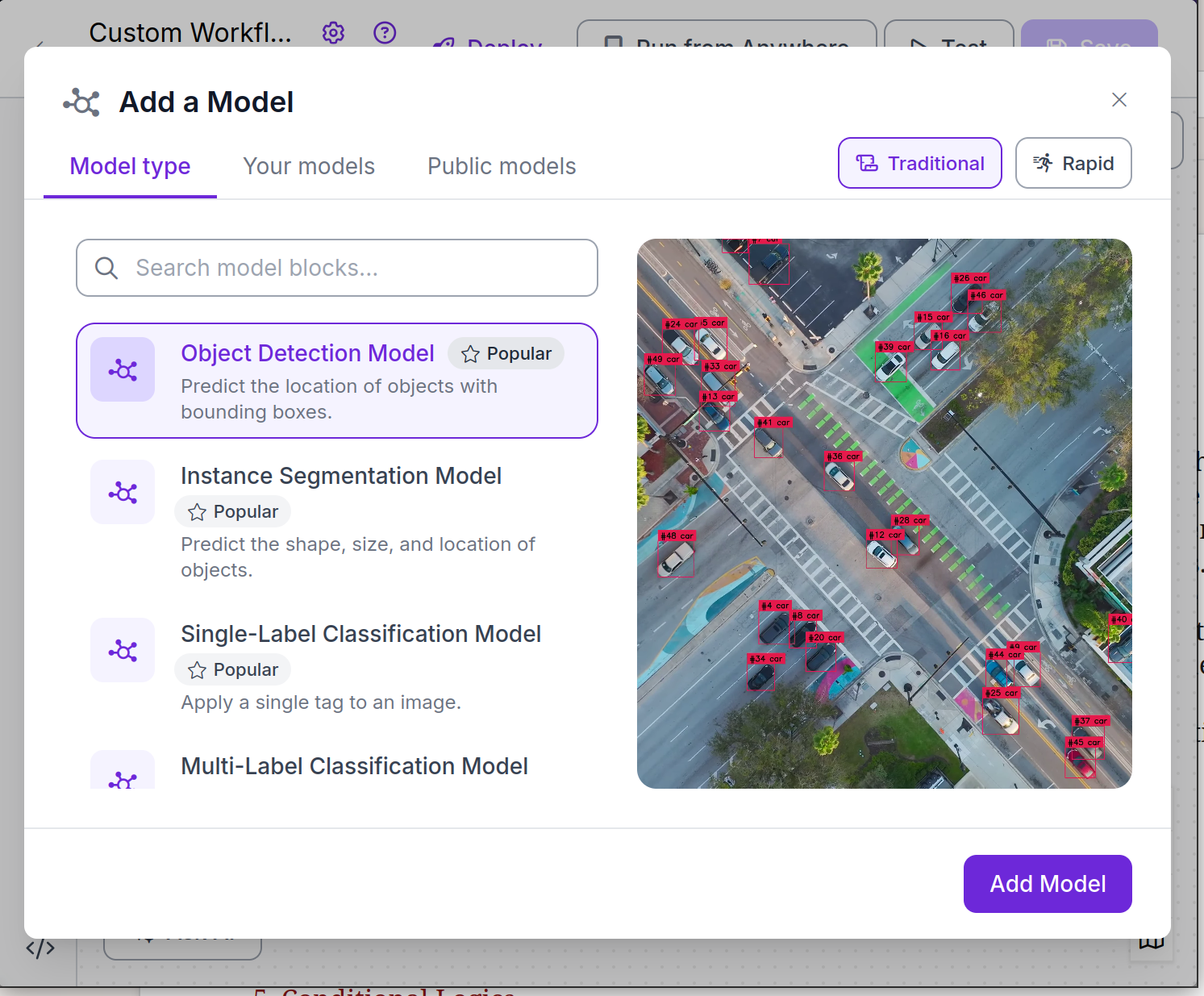
For the model, any will do, but we'll pick YOLOv8.
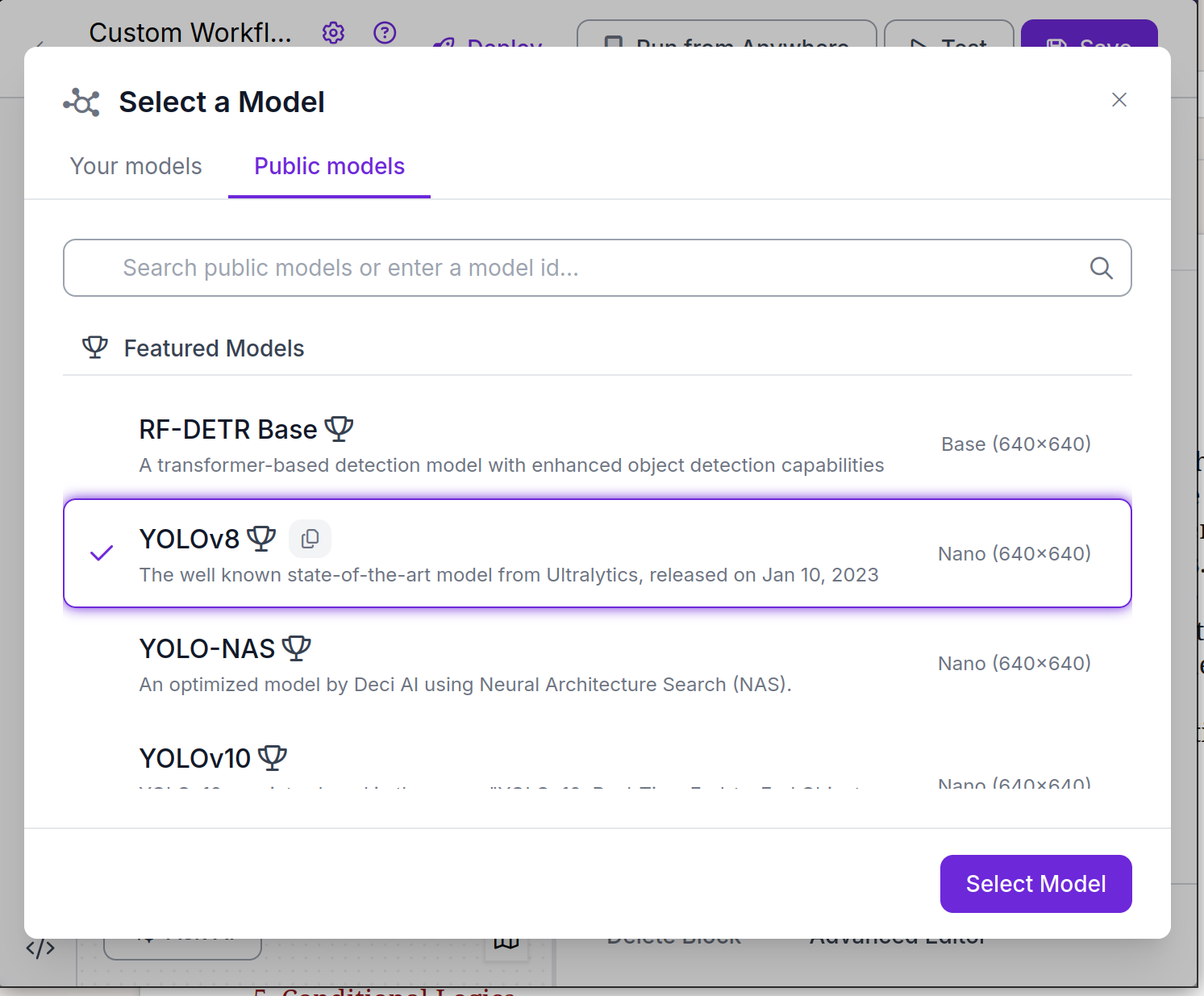
Once we choose the model, Roboflow will show us a graphical view of our workflow. The workflow can be edited from here, but the default layout is fine for our task.
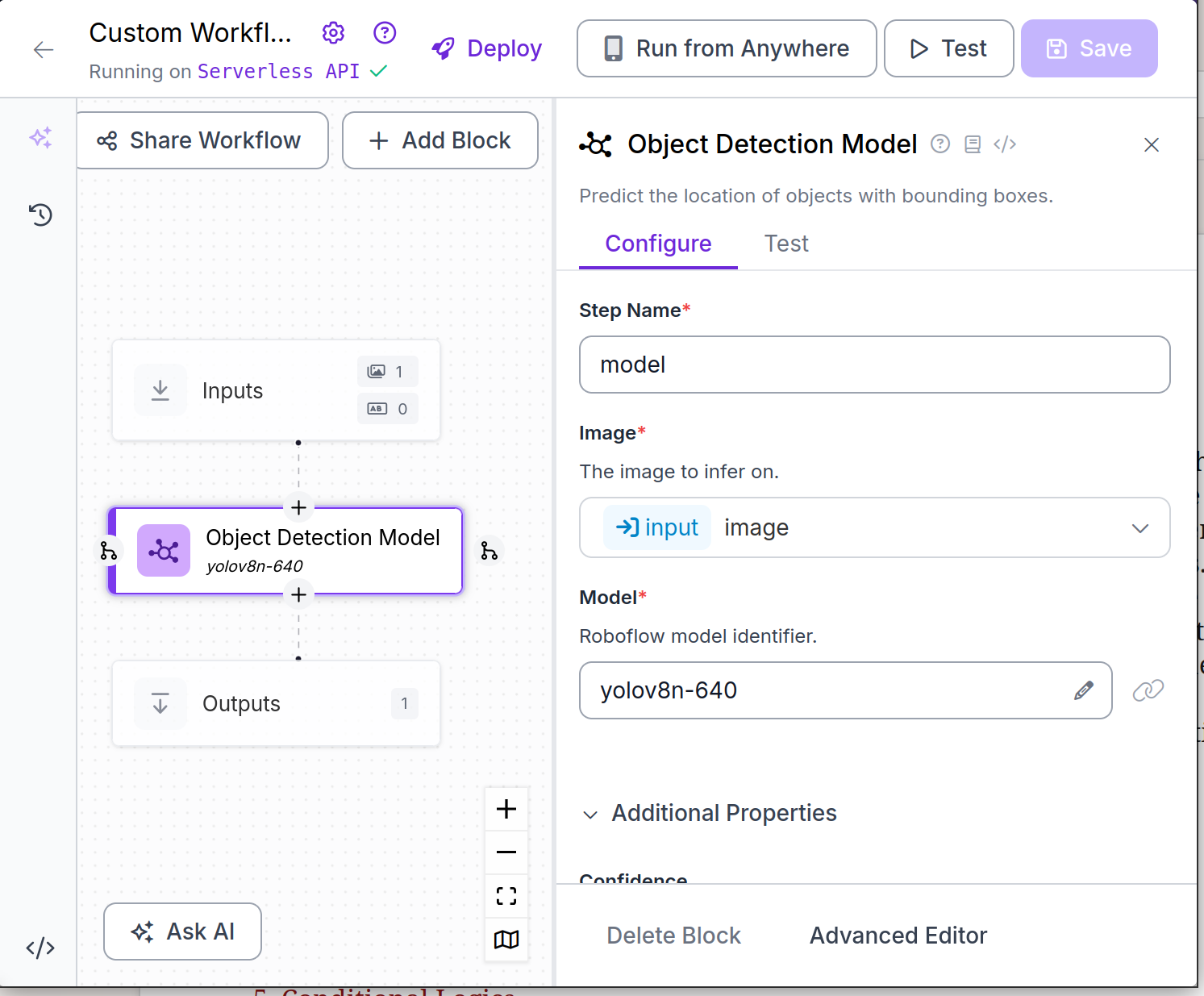
We can click on the test button at the top bar to test our model with static images. Once we have the model test page open, we'll see a button that says "Ready to deploy?".
By clicking the "Ready to deploy?" button, we get a page that allows us to call our model remotely.
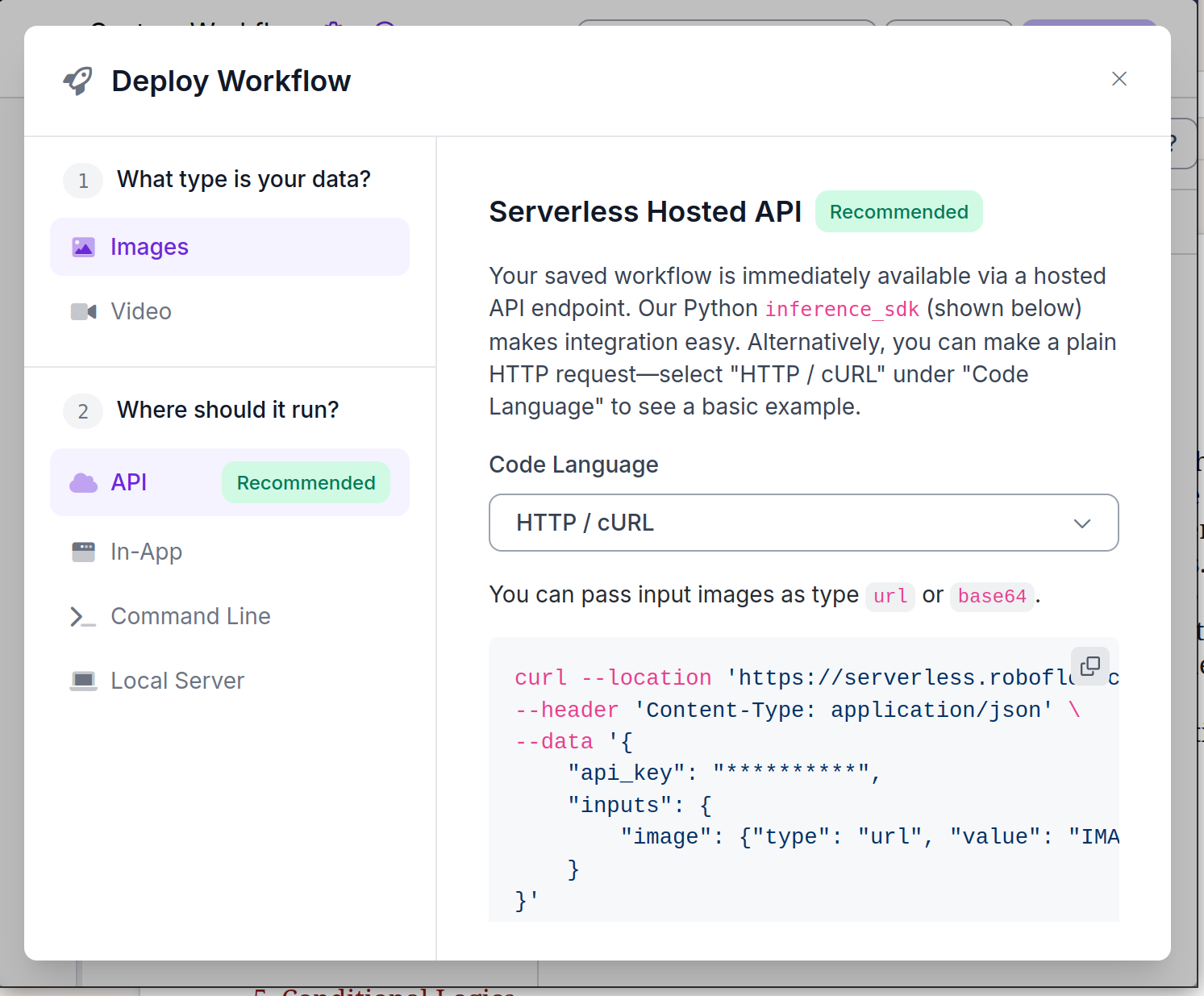
We'll use the HTTP / cURL version of the API call and use the Java HTTP library to send the image from BarcodeSink.
Sending Images to Roboflow
Now we'll use BarcodeSink to pull images off the camera and send them to our Roboflow workflow. First, we'll subclass CameraServer. We'll add arguments to the constructor to pass the Roboflow URI and API key in. The subclass will override the onMessage method to encode the data as base64, open a HTTP client connection to roboflow, and send it to Roboflow. The code is several lines, but most of it is building up the JSON object to send.
public class CameraServerRoboflow extends CameraServer {
private String roboflowKey;
private URI roboflowLocation;
public CameraServerRoboflow(InetSocketAddress address, URI roboflowLocation, String roboflowKey) throws IOException {
super(address);
this.roboflowLocation = roboflowLocation;
this.roboflowKey = roboflowKey;
}
@Override
protected void onMessage(CameraInfo connection, CameraScanResult result) {
sendImageToRoboflow(result);
}
private void sendImageToRoboflow(CameraScanResult result) {
try {
String writerName = "BMP";
ByteArrayOutputStream output = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
boolean isWriter = ImageIO.write(result.getImage(), writerName, output);
String imageString = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(output.toByteArray());
JSONObject jsonImage = new JSONObject();
jsonImage.put("type", "base64");
jsonImage.put("value", imageString);
JSONObject jsonInputs = new JSONObject();
jsonInputs.put("image", jsonImage);
JSONObject jsonRoot = new JSONObject();
jsonRoot.put("inputs", jsonInputs);
jsonRoot.put("api_key", roboflowKey);
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newBuilder()
.version(Version.HTTP_1_1)
.followRedirects(Redirect.NORMAL)
.connectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(20))
.build();
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(roboflowLocation)
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.POST(HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofString(jsonRoot.toString(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
.timeout(Duration.ofMinutes(1))
.build();
HttpResponse response = client.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
System.out.println(response.statusCode());
System.out.println(response.body());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
That's it. With Roboflow set up we can now succesfully send data.
Workflow Output
Now that we have the camera sending images to Roboflow we can view the data coming out. After scanning a book with a barcode, the predictor detected an image and sent it back to us.
{
"outputs": [
{
"model_predictions": {
"image": {
"width": 1024,
"height": 768
},
"predictions": [
{
"width": 613.0,
"height": 362.0,
"x": 716.5,
"y": 306.0,
"confidence": 0.5204567909240723,
"class_id": 73,
"class": "book",
"detection_id": "e4a035a4-4a35-40ca-aa21-5d5654aee480",
"parent_id": "image"
}
]
}
}
],
"profiler_trace": []
}
If you want to repurpose existing Cognex Dataman devices to use Roboflow, or any other computer vision system, without changing out hardware, BarcodeSink can help.